Hidden Lyme Causes Brain Fog and Depression
- Home
- Blog

My Dear Reader,
If you or someone you love has been suffering from symptoms of Brain Fog and Depression that have persisted despite treatment, you may be suffering from a hidden cause related to Lyme Disease or other tickborne illnesses like Babesia or Bartonella. Please read on to learn more about how this can be diagnosed and treated.
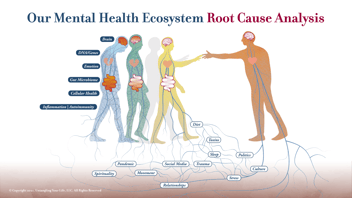
Introduction: In the quest for emotional well-being and mental clarity, understanding the root causes of psychiatric conditions is paramount. Often, the sources of ailments like depression and brain fog lie concealed, evading detection and complicating treatment. One such hidden adversary is Lyme Disease, along with other tickborne illnesses such as Babesia and Bartonella. At Potomac Psychiatry, we delve into the depths of these hidden causes, offering hope and solutions through our Root Cause Psychiatry™ Program.
The Unseen Culprit: Lyme Disease and Brain Fog Lyme Disease, caused by the Borrelia burgdorferi bacterium transmitted through tick bites, is commonly associated with physical symptoms like rash, fever, and joint pain. However, its impact on mental health, manifesting months or even years after the initial tick bite, often goes unrecognized. The insidious nature of this disease means many sufferers may not recall being bitten by a tick, leading to misdiagnosis or delayed treatment.
Symptoms of Lyme-Induced Psychiatric Conditions:
- Depression: A deep-seated sense of despair and disinterest, often unresponsive to traditional depression treatments. This can include withdrawing from others, too little or too much sleep, and even crying spells and feelings of helplessness and hopelessness.
- Brain Fog: A troubling lack of mental clarity, characterized by confusion, forgetfulness, and difficulty concentrating. Sometimes even trouble sustaining a focus, easy distractibility and word finding difficulties may be present.
- Other Cognitive and Emotional Issues: Mood swings, anxiety, and cognitive impairments, further complicating the individual's daily life. This may also include panic attacks or OCD symptoms.
Persisting Infection, Reactivated Infection, Brain Inflammation
Understanding the impact of Lyme Disease on mental health requires an exploration into the complex ways this infection interacts with our brain and nervous system. Mental health effects can arise from a persisting Lyme infection, a reactivation of the infection, or because of brain inflammation triggered by the body's immune response to the infection. Scientific studies have shed light on these connections. For instance, research published in the 'Journal of Medical Microbiology' (Marques, 2015) suggests that persisting Lyme infection can lead to neurological complications due to direct infection of the central nervous system. Furthermore, a study in 'Frontiers in Neurology' (Aucott, Rebman, Crowder, & Kortte, 2013) indicates that reactivation of Lyme infection can trigger neuropsychiatric symptoms. Lastly, the role of brain inflammation in Lyme Disease-related cognitive impairments is highlighted in 'Brain, Behavior, and Immunity' (Kadam, Morisseau, & Hammock, 2017), where neuroinflammatory processes are implicated in the causation of psychiatric symptoms. These insights underscore the necessity of considering Lyme Disease in a Root Cause Psychiatry™ approach to unexplained psychiatric symptoms and the importance of timely, targeted intervention.
Diagnostic Testing, Treatment, and the Hope of Recovery
In a prior blog I wrote about how infectious diseases are among the root causes of psychiatric conditions, and Lyme Disease is no exception. At Potomac Psychiatry, our approach to diagnosing and treating the psychiatric manifestations of Lyme Disease and other tickborne illnesses is both comprehensive and cutting-edge. To accurately diagnose these conditions, we utilize advanced tests like the IgeneX Tickborne Diseases 6IBL panel, which offers a thorough assessment of various tickborne infections. This detailed testing is crucial for uncovering the often-overlooked link between tickborne diseases and mental health symptoms. We may also use The Cunningham Panel to look for a hidden autoimmune condition where antibodies to Lyme bacterium also attack the brain. Once a diagnosis is established, our treatment strategies are multifaceted and tailored to each individual's needs. Treatment may include a combination of antidepressants to address mood symptoms, anti-inflammatory medications to reduce brain inflammation, immune system modulating medications to correct immune dysregulation, and antibiotics to target the underlying infection. This integrative treatment approach, which may include nutritional guidance and lifestyle modifications, ensures that we address both the root cause of the infection and its psychiatric effects, paving the way for holistic healing and recovery..
Support and Guidance: The path to healing is not one to walk alone. Our team provides continuous support, understanding, and expertise, ensuring that each step taken is one towards recovery and wholeness.
Conclusion: Lyme Disease is a hidden challenge with far-reaching consequences for mental health. But within this challenge lies the opportunity for profound healing and growth. At Potomac Psychiatry, we're committed to guiding our patients through this journey, uncovering hidden causes, and restoring mental clarity and emotional well-being. If you or a loved one is struggling with symptoms that defy explanation, we're here to offer hope and help.
Ready to embark on a journey of healing and discovery? Book your no-cost consultation with us today and learn more about our Root Cause Psychiatry Program at Potomac Psychiatry.
.png?width=144&height=144&name=Untitled%20design%20(34).png)